As a result of several years of research, the American Heart Association has created new hypertension guidelines.
Do you know what hypertension is?
Almost every visit to the doctor means getting a blood pressure test. If your blood pressure is high, your doctor may diagnose you with hypertension. High blood pressure is the leading risk factor in heart disease and strokes, and is a contributing cause of death in 1,100 deaths in the U.S. every day.
Even children are at risk, although it is most common with adults. In particular, with the rise of childhood obesity, more and more kids are becoming at risk.
The CDC reported in 2014 that 1 in 3 American adults have higher blood pressure numbers than normal, and another third have hypertension.
What is Star Access? Star Access provides direct laboratory testing for individuals. Order your lab test now.
This spring, the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and nine other health organizations looked at the guidelines for hypertension. This was the first time in over a decade that treating this disease received such an extensive review. As a result, blood pressure parameters for this common condition have changed dramatically. Under these new numbers, a large number of Americans – previously undiagnosed as having high blood pressure – now have hypertension.
What You Need to Know About Hypertension
Research since 2003 showed a growing trend of hypertension in Americans and a need for new guidelines. At-risk behavior was not addressed soon enough, giving the disease a “head start” when treatment began. The new guidelines help people more quickly address their high blood pressure issues. These instructions were written by a panel of 21 scientists and health experts who reviewed more than 900 scientific studies.
Along with new thresholds, the panel proposed a few other suggestions. The new guidelines highlight the importance of proper and exact measuring and an emphasis on habit change over medication. In fact, Stage 1 hypertension, under these new guidelines, is only treated with medication if the patient has had a cardiovascular event or is at high risk for one.
To stave off “white-coat hypertension” the organization advocates for better training to keep patients calm so they may gather correct blood pressure readings. Training is also important for the precise way in which blood pressure tests should be administered – including the patient’s feet flat on the floor and the test taken from a hanging, not bent, arm.
They also propose increased use of validated home devices for more continuous blood pressure monitoring. Harvard Health published a recent paper outlining what proper home recording is and how to do it. Again, proper readings only come from properly administered tests and machines.
The Changes, and Their Effects on Care
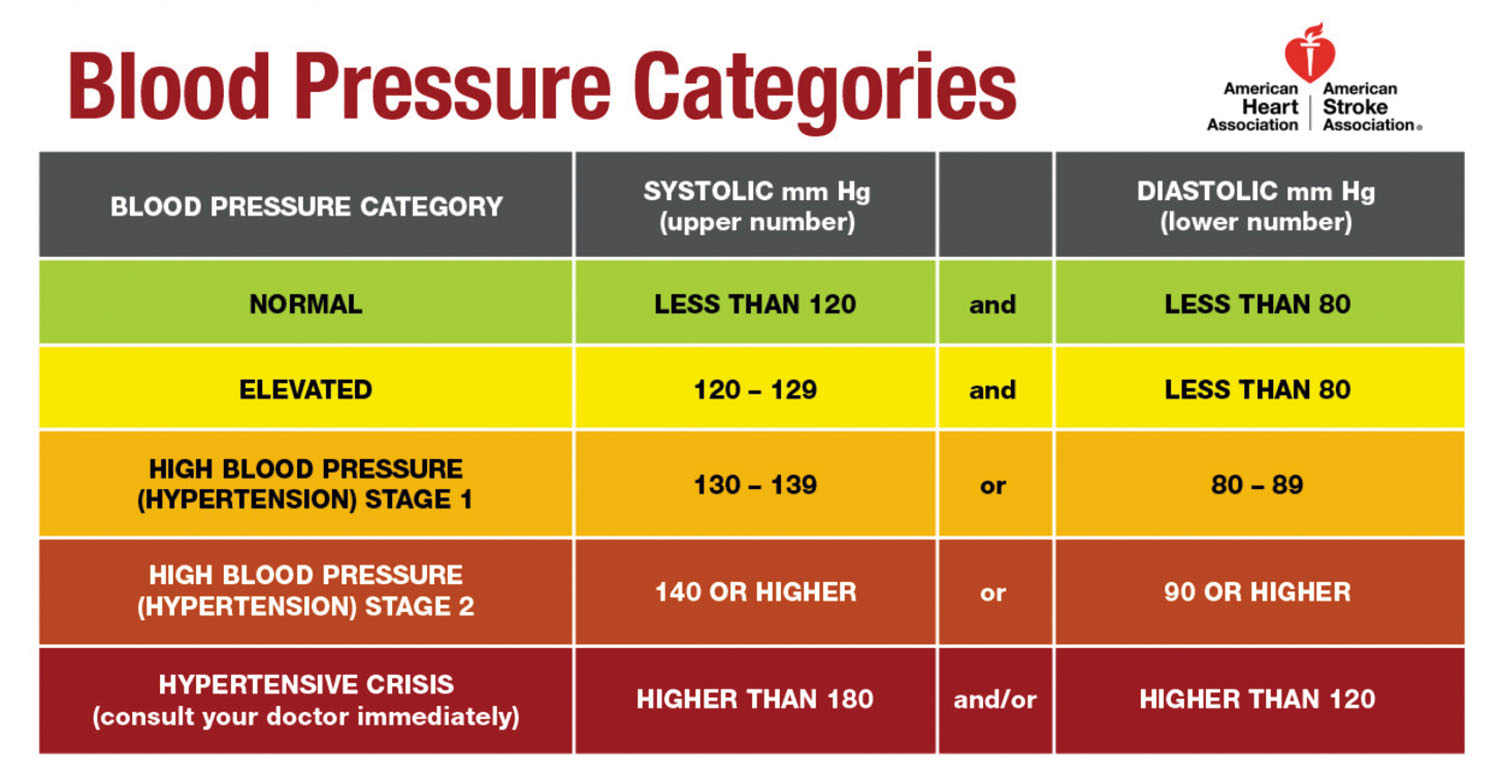
The most noticeable difference in the new guidelines is the lack of the phrase “prehypertension.” A reading below 120/80 mm Hg is still considered a normal blood pressure. If the second number (the diastolic) is higher than 80 – this is now considered either Stage 1 or Stage 2 hypertension. (Stage 1 is less than 90 mm Hg, Stage 2 is higher.)
If the diastolic reading is below 80 mm Hg, but the first number, the systolic, is above normal – the patient is considered at an “elevated risk” for hypertension. Stage 1 for this number begins at a reading of 130, Stage 2 begins at 140.
What do these numbers mean? The first number is the amount of pressure the blood is under from a heart beat. When the chambers move the blood, that is that higher, first number. The second number is the pressure of the blood in between beats, when it’s at rest. When your heart beats, it pushes blood out with a strong force – that’s your higher number. After that initial push, there’s no suction or other way for blood to return to the heart, except that the heart is pumping new blood behind it. The second smaller number measures that force, the force of the blood being pushed back to the heart.
These new numbers mean many more Americans now have hypertension. Stage 1 hypertension previously began where Stage 2 now begins. Under the new guidelines for elevated risk and Stage 1 hypertension, medication is rarely prescribed. There are only a few instances where a patient with Stage 1 hypertension would receive medication.
New Ideas From Research
Pouring over the numbers, two new, possibly game-changing, ideas came to light. The first was an overwhelming nod that many people require two or more pills to combat hypertension. This realization gives the prescribing doctor more flexibility to treat the patient. Instead of looking for one “cure-all” drug, the team can look for more effective ways to address the disease.
Also to come to light since 2003, the importance of socioeconomic factors and psychosocial stress as risk factors was evident. The new guidelines highlight these as important in all decision-making when dealing with hypertension. A patient’s plan of care must also include these risk factors for a complete health picture and also for best results.
Star Wellness offers easy-to-order health screening for individuals. Our mission is to save lives by alerting individuals to health conditions of which they were previously unaware. By watching the latest guidelines, like these recent new hypertension guidelines, we give the best and newest information to our customer.